Until now I didn't find a 64bit version of the AMD AHCI driver v6.1.3.35. If anyone should have a link, please let me know it. Whose Intel SATA Controller has been set to RAID mode. (wrong) Vista/Win7 instead of the correct Windows XP AMD AHCI driver. The driver named amd_sata.sys can only be used with Operating Systems from Vista up. This issue can occur when SATA controller gets default Windows drivers and if the. Config to put SATA mode into IDE, rather than AHCI, WinPE will load just fine. Image so that I can use it with the SATA mode left in its standard AHCI mode?' Faced was: No AMD Sata Driver support in WINPE Intel CPU driver conflict. Chipset sata controller driver. Need help updating standard SATA AHCI Controller driver. Solved Should I use Intel SATA Controller Driver instead of Windows 8.1 Inbuilt Driver to get best. Find or download F6 textmode AHCI driver for your SATA controller. Find out the name of your chipset (south bridge). It should be in the user guide of your motherboard or notebook, or at the manufacturer's website. I have a Gigabyte F2A85X motherboard. So recently i was checking the Device Manager and saw that 'Standard SATA AHCI Controller' driver was of 2006. The first device, on my system, is using an 'AMD SATA Controller' driver from 3/29/2015, so it's been around for a good while (which explains why even somewhat older Linux kernels support it natively, but Windows 7 does not). The second device uses the Microsoft 'Standard SATA AHCI Controller driver.'
| Advanced Host Controller Interface | |
| Website | www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/io/serial-ata/ahci.html |
|---|---|
Oct 17, 2016 - You will see a few entries and if you are using the Intel drivers in AHCI mode. And containing AHCI, e.g. Intel(R) ICH10D/DO SATA AHCI Controller. The Microsoft driver will now be installed and you will need to do a restart. If you have an AMD chipset, it is a good idea to check AMD's website instead.
The Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the operation of Serial ATA (SATA) host controllers in a non-implementation-specific manner in its motherboard chipsets.
The specification describes a system memory structure for computer hardware vendors to exchange data between host system memory and attached storage devices. AHCI gives software developers and hardware designers a standard method for detecting, configuring, and programming SATA/AHCI adapters. AHCI is separate from the SATA 3 Gbit/s standard, although it exposes SATA's advanced capabilities (such as hot swapping and native command queuing) such that host systems can utilize them.
As of March 2014, the current version of the specification is 1.3.1.
- 2Operating System Support
Operating Modes[edit]
Many SATA controllers offer selectable modes of operation: legacy Parallel ATA emulation (more commonly called IDE Mode), standard AHCI mode (also known as Native Mode), or vendor-specific RAID (which generally enables AHCI in order to take advantage of its capabilities). Intel recommends choosing RAID mode on their motherboards (which also enables AHCI) rather than AHCI/SATA mode for maximum flexibility.[1] Legacy mode is a software backward-compatibility mechanism intended to allow the SATA controller to run in legacy operating systems which are not SATA-aware or where a driver does not exist to make the operating system SATA-aware.
When a SATA controller is configured to operate in Legacy Mode, the number of storage devices per controller is usually limited to four (two IDE channels, primary and secondary, with up to two devices per channel), compared to the maximum of 32 devices/ports when configured in AHCI mode.[2][3]
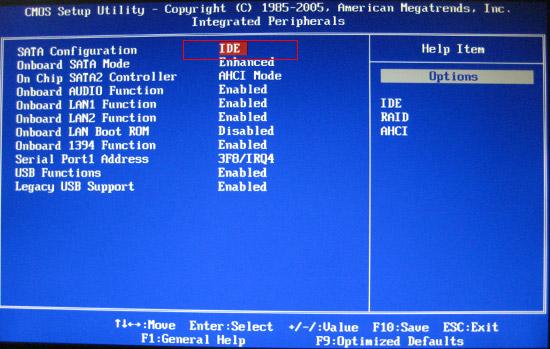
Operating System Support[edit]
AHCI is supported out of the box on Windows Vista and later, Linux-based operating systems (since version 2.6.19 of the kernel), OpenBSD (since version 4.1), NetBSD (since version 4.0), FreeBSD (since version 8.0), macOS, eComStation (since version 2.1), and Solaris 10 (since version 8/07).[4]DragonFlyBSD based its AHCI implementation on OpenBSD's and added extended features such as port multiplier support. Older versions of operating systems require hardware-specific drivers in order to support AHCI. Windows XP and older do not provide AHCI support out of the box.
System Drive Boot Issues[edit]
Some operating systems, notably Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, do not configure themselves to load the AHCI driver upon boot if the SATA controller was not in AHCI mode at the time the operating system was installed. Although this is an easily rectifiable condition, it remains an ongoing issue with the AHCI standard.
The most prevalent symptom for an operating system (or systems) that are installed in IDE mode (in some BIOS firmware implementations otherwise called 'Combined IDE mode'), is that the system drive typically fails to boot, with an ensuing error message, if the SATA controller (in BIOS) is inadvertently switched to AHCI mode after OS installation. In Microsoft Windows the symptom is a boot loop which begins with a Blue Screen error, if not rectified - and through no fault of the Windows OS.
Technically speaking, this is an implementation bug with AHCI that can be avoided, but it has not been fixed yet. As an interim resolution, Intel recommends changing the drive controller to AHCI or RAID before installing an operating system.[1] (It may also be necessary to load chipset-specific AHCI or RAID drivers at installation time, for example from a USB flash drive).
On Windows Vista and Windows 7, this can be fixed by configuring the msahci device driver to start at boot time (rather than on-demand). Setting non-AHCI mode (i.e. IDE or Combined mode) in the BIOS will allow the user to boot into Windows, and thereby the required registry change can be performed. Consequently, the user then has the option of continuing to use the system in Combined mode or switching to AHCI mode.[5]With Windows 10, this can be fixed by forcing the correct drivers to reload during Safe Mode.[6]
In Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012, the name of the controller has changed from msahci to storahci,[7] and the procedures to upgrade to the new controller is similar to that of Windows 7.[8] On Windows 8, 8.1 and Windows Server 2012, changing from SATA mode to AHCI mode without first updating the registry will make the boot drive inaccessible (i.e. resulting in a recurring boot loop, which begins with a Blue Screen error).
A similar problem can occur on Linux systems if the AHCI driver is compiled as a kernel module rather than built into the kernel image, as it may not be included in the initrd (initial RAM disk) created when the controller is configured to run in Legacy Mode. The solution is either to build a new initrd containing the AHCI module, or to build the AHCI driver into the kernel image.[9]
Power management[edit]
Power management is handled by the Aggressive Link Power Management (ALPM) protocol.
See also[edit]
- Open Host Controller Interface (OHCI)
- Universal Host Controller Interface (UHCI)
- Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI)
- Extensible Host Controller Interface (XHCI)
- NVM Express (NVMe)
- Wireless Host Controller Interface (WHCI)
References[edit]
- ^ ab'Intel Matrix Storage Technology - Changing and/or choosing Serial ATA Modes'. Intel. Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ^'PCI IDE Controller Specification 1.0'(PDF). Berg Software Design. Retrieved 2015-05-03.
- ^'Serial ATA AHCI: Specification, Rev. 1.3.1'. Intel Corp. Retrieved 2015-05-03.
- ^'What's New in the Solaris 10 8/07 Release - Driver Enhancements'. Oracle. Retrieved 2010-10-20.[permanent dead link]
- ^'Error Message when you start a Windows 7 or Windows Vista-based computer after you change the SATA mode of the boot drive: 'STOP 0x0000007B INACCESSABLE_BOOT_DEVICE''. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 2011-04-20.
- ^'Enabling AHCI mode AFTER Windows 10 installation'. tenforums.com user Toobad. Retrieved 2015-12-19.
- ^'StorAHCI replaces MSAHCI (Windows)'. Microsoft.
- ^'Improving performance of SATA drives on Windows 2012'.
- ^'Support | How to enable AHCI support after install'. Novell.com. Retrieved 2014-05-11.
Amd Sata Controller Driver Update
External links[edit]
- 'AHCI Specification'. Intel.
- 'AHCI'. OSDev Wiki